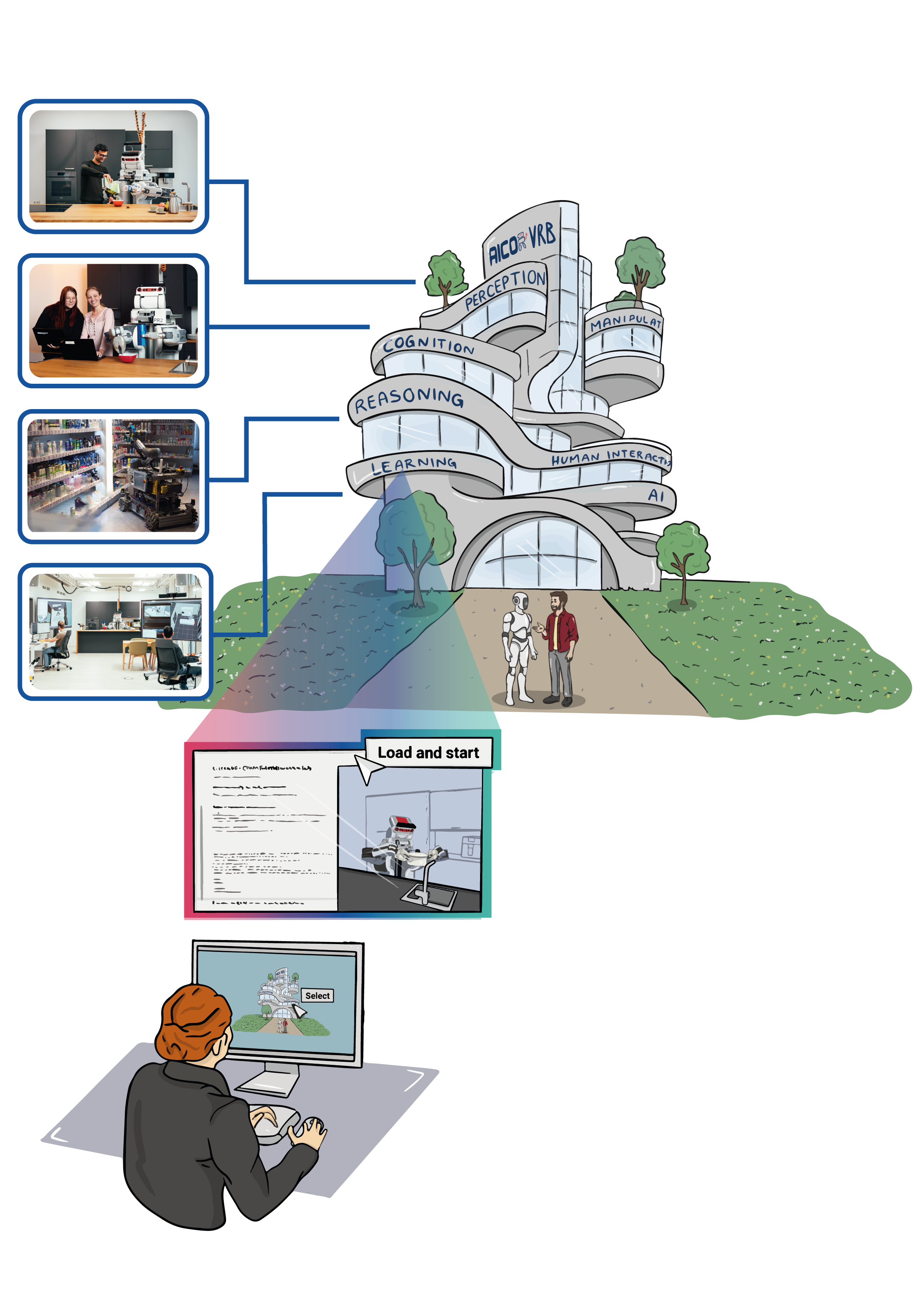
In this virtual research lab, we aim to empower robots with the ability to understand the ‘what’ and ‘how’ of task demonstrations so that robots are enabled to reason about logged memories and differentiate between performed tasks, particularly in everyday manipulations like cutting or pouring. By integrating actionable knowledge graphs, robots are enabled to link contained object and environment information to ation information and map the information to the parameters from their generalized action plans. These plans then enable robots to adapt cutting techniques such as slicing, quartering, and peeling as looged in the task demonstrations, allowing for more specialised task execution.
In the laboratory below, you have the opportunity to select a VR task demonstration to then explore actionable knowledge graph content tailored to specific task domains, including fruit cutting, by utilizing resources like Wikipedia, biology textbooks, nutrition information sources, and instructional websites such as WikiHow. Additionally, you’ll have access to a comprehensive robotic action plan designed specifically for fruit cutting tasks. The integration of actionable knowledge graph information with the task demonstration, such as ”quartering an apple,” can be translated into specific action parameters of the robot. The customized plan can be tested and refined within a simulated environment.


Michaela Kümpel (Knowledge Graphs) and Abhijit Vyas (VR Demonstrations) and Vanessa Hassouna (Robot Action Execution)
Tel: +49 421 218 64021, +49 421 218 64026, +49 421 218 99651Mail: michaela.kuempel@cs.uni-bremen.de, avyas@cs.uni-bremen.de ,hassouna@cs.uni-bremen.de
Profile Michaela Kümpel Profile Abhijit Vyas Profile Vanessa Hassouna
Interactive Actions and/or Examples
In this lab, we want to show how robots can perform task learning.
To achieve our goal of enabling a robotic agent to learn tasks from human demonstrations, we follow the idea below, which is also described in
Kümpel, Michaela, Vyas, Abhijit, Hassouna, Vanessa and Beetz, Michaela, “Task Learning Using Actionable Knowledge Graphs”, In ICRA40- 40th Anniversary of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2024.

Our framework consists of two steps.
Step 1 is to select and load an episodic memory/ human task demonstration from our logged experience database and query it for task information. This can be done in the following notebook:
Load and Query the Virtual Reality Demonstrations NEEMs Load NEEM
Step 2 is to use the parameters for action parametrisation of the robot action plan. This is done in the following notebook:
Query the Robot Demonstrations
Run Code
References
[^1] M. Kümpel et al., ‘Task Learning Using Actionable Knowledge Graphs’, in ICRA40- 40th Anniversary of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2024.